Abstract
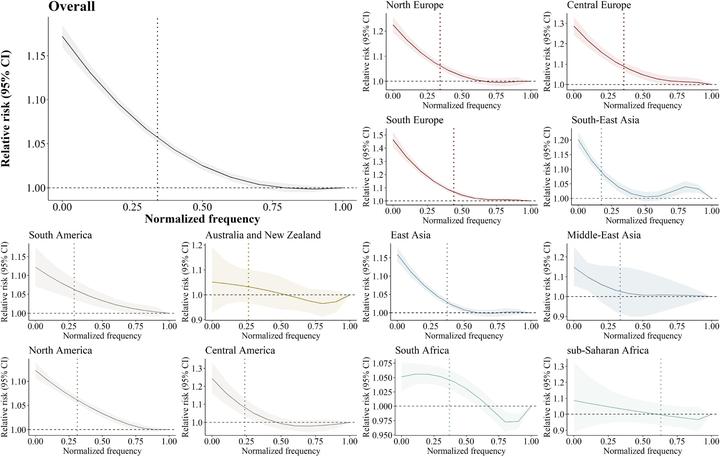
Assessing the association between temperature frequency and mortality can provide insights into human adaptation to local ambient temperatures. We collected daily time-series data on mortality and temperature from 757 locations in 47 countries/regions during 1979–2020. We used a two-stage time series design to assess the association between temperature frequency and all-cause mortality. The results were pooled at the national, regional, and global levels. We observed a consistent decrease in the risk of mortality as the normalized frequency of temperature increases across the globe. The average increase in mortality risk comparing the 10th to 100th percentile of normalized frequency was 13.03% (95% CI: 12.17–13.91), with substantial regional differences (from 4.56% in Australia and New Zealand to 33.06% in South Europe). The highest increase in mortality was observed for high-income countries (13.58%, 95% CI: 12.56–14.61), followed by lower-middle-income countries (12.34%, 95% CI: 9.27–15.51). This study observed a declining risk of mortality associated with higher temperature frequency. Our findings suggest that populations can adapt to their local climate with frequent exposure, with the adapting ability varying geographically due to differences in climatic and socioeconomic characteristics.